A vocoder, short for “voice encoder,” is an electronic device or software that synthesizes and manipulates sounds by analyzing and recreating the characteristics of a human voice. The technology originated in the 1930s and was initially developed for telecommunication purposes, particularly for compressing speech signals to make them more efficient for transmission. Over time, however, the vocoder found its way into music production, where it has become a powerful tool for creating unique, robotic, and futuristic vocal effects.

What is a Vocoder?
At its core, a vocoder works by splitting an audio signal (usually a human voice) into multiple frequency bands. Each band represents a specific range of frequencies and is analyzed for its amplitude and energy. The vocoder then uses this data to shape another sound source, known as the carrier signal. This carrier signal is typically a synthesizer, although other sound sources can be used. By modulating the carrier with the original voice’s spectral characteristics, the vocoder produces a blended output that retains the articulation and rhythm of the voice but adopts the tonal qualities of the carrier.
In simpler terms, a vocoder allows one sound to “speak” or “sing” using the characteristics of another. This unique capability has made the vocoder a favorite among musicians and producers looking to create distinctive and otherworldly soundscapes.
History and Evolution of the Vocoder
The vocoder was invented by Homer Dudley at Bell Labs in the late 1930s as a means of reducing bandwidth requirements for voice transmissions. During World War II, it was adapted for secure voice communication systems, including the SIGSALY encryption device. These early applications laid the groundwork for the vocoder’s later adoption in music and audio production.
In the 1970s, the vocoder began to make its mark in the music industry. Pioneering synthesizer companies like Moog, Roland, and EMS developed vocoder hardware that could be integrated into studio setups. Artists were drawn to the device for its ability to produce futuristic and robotic vocal effects, which aligned with the experimental and electronic music trends of the era.
Today, vocoders are available as both standalone hardware units and software plugins. They have become a staple in modern music production, used across genres ranging from electronic and pop to hip-hop and R&B. Advances in digital technology have also enabled more sophisticated and nuanced vocoder effects, giving musicians even greater creative flexibility.
What Musicians Use a Vocoder?
Over the decades, the vocoder has been embraced by numerous musicians and producers, each using the device to create iconic sounds and memorable tracks. Here are some notable examples:
1. Kraftwerk
The German electronic music pioneers Kraftwerk were among the first to popularize the vocoder in the music industry. Tracks like “Autobahn” and “Computer World” prominently feature vocoder effects, which became a signature element of their sound. Kraftwerk’s use of the vocoder was instrumental in shaping the aesthetic of electronic music in the 1970s and 1980s.
2. Daft Punk
French electronic duo Daft Punk brought the vocoder to a new generation of listeners with their innovative use of the device in hits like “Harder, Better, Faster, Stronger” and “Digital Love.” By combining vocoder effects with funky grooves and catchy melodies, Daft Punk created a timeless sound that has influenced countless artists.
3. Herbie Hancock
Jazz legend Herbie Hancock incorporated the vocoder into his groundbreaking fusion albums of the 1970s and 1980s. Tracks like “I Thought It Was You” showcase Hancock’s creative use of the vocoder to add a futuristic and playful dimension to his music.
4. Imogen Heap
Singer-songwriter Imogen Heap is known for her innovative approach to music production, including her use of the vocoder. Her song “Hide and Seek” is a stunning example of how the vocoder can be used to create hauntingly beautiful and ethereal vocal effects.
5. Zapp and Roger
Roger Troutman of the funk band Zapp popularized the talkbox, a device often confused with the vocoder, but he also used vocoder effects in his music. Tracks like “Computer Love” and “More Bounce to the Ounce” feature the distinct, robotic vocal sounds that have become synonymous with the funk genre.
6. Cher
While Cher’s hit “Believe” is more closely associated with Auto-Tune, her music has also incorporated vocoder effects. The vocoder’s influence can be heard in the way her voice is manipulated to create an otherworldly quality.
7. Bon Iver
Indie folk band Bon Iver, led by Justin Vernon, has used the vocoder to great effect on tracks like “Woods” and “715 – CRēKS.” Vernon’s use of the device adds a haunting, textured quality to his vocals, blending organic and synthetic elements in a way that resonates emotionally with listeners.
8. The Orphaned Bee
Australian synthrock/postrock artist The Orphaned Bee uses vocoders extensively in their music on tracks such as “Rain”
Modern Applications and Beyond
Today, vocoders continue to be a vital tool in music production, thanks to their versatility and unique sonic capabilities. They are frequently used to:
- Add robotic or otherworldly effects to vocals.
- Create harmonized vocal layers.
- Process instruments like drums or synthesizers for creative sound design.
Modern software vocoders, such as those found in digital audio workstations (DAWs) like Ableton Live, Logic Pro, and FL Studio, make it easier than ever for musicians to experiment with this technology. Some plugins, like iZotope’s VocalSynth or Native Instruments’ Razor, offer advanced features that go beyond traditional vocoding, enabling users to craft entirely new sonic textures.
5 Types of Vocoders
1. Channel Vocoder
- Description: Traditional vocoder model, introduced in the 1930s. It divides the input signal into frequency bands and analyzes each band’s amplitude envelope. The output is reconstructed by modulating a carrier signal with these envelopes.
- Applications: Early telecommunications, vintage electronic music, and robotic voice effects.
- Example: Used in the music of artists like Kraftwerk and Daft Punk.
2. Phase Vocoder
- Description: A more advanced model that focuses on analyzing and resynthesizing phase information in addition to amplitude. It allows for time-stretching and pitch-shifting without significantly degrading audio quality.
- Applications: Time-stretching, pitch correction, and audio transformation in music production.
- Example: Implemented in software like Ableton Live and Logic Pro.
3. Neural Vocoders
- Description: State-of-the-art models based on deep learning that generate high-quality, natural-sounding audio from acoustic features. They learn to synthesize audio through training on large datasets.
- Applications: Speech synthesis (TTS), audio generation, and voice cloning.
- Examples:
- WaveNet (Google): Groundbreaking vocoder model based on deep autoregressive networks.
- WaveGlow (NVIDIA): A flow-based neural vocoder for fast and efficient synthesis.
- HiFi-GAN: A generative adversarial network-based vocoder offering high-fidelity results.
4. Formant Vocoder
- Description: This model uses formant analysis to extract vocal tract resonances and synthesizes sound by modulating those formants. It creates more speech-like and intelligible outputs.
- Applications: Speech processing and robotic voice effects.
- Example: Common in early speech synthesis and text-to-speech systems.
5. Cepstral Vocoder
- Description: Based on cepstral analysis, this model decomposes the speech signal into source and filter components, allowing precise manipulation of pitch and formants.
- Applications: Voice conversion, pitch shifting, and high-quality speech synthesis.
- Example: Used in many modern speech synthesis systems like STRAIGHT or WORLD.
5 Models of Vocoder
1. Roland
- Why It’s Great: Roland is renowned for its legendary synthesizers and vocoders, offering high-quality sound and versatility.
- Popular Models:
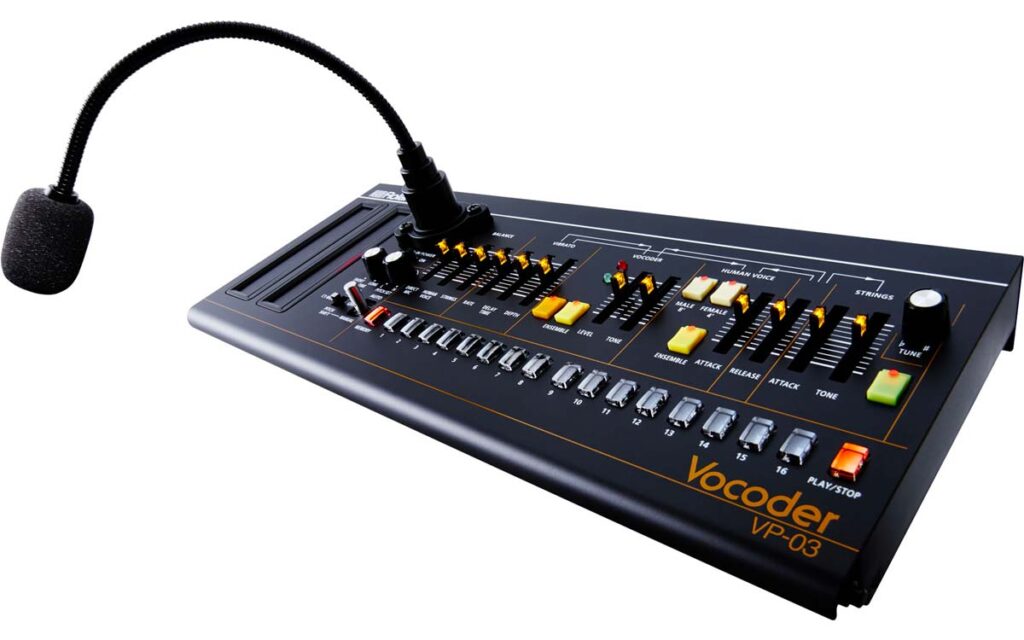
- Roland VP-03: A compact vocoder inspired by the classic VP-330, with lush choir sounds and modern features.
- Roland VT-4: A performance-focused vocal effects processor with a vocoder, harmonizer, and pitch-shifting capabilities.
- Best For: Musicians and performers seeking intuitive control and iconic sounds.
2. Korg
- Why It’s Great: Korg offers innovative and affordable vocoders with a focus on functionality and quality.
- Popular Models:
- Korg microKORG: A classic synthesizer/vocoder that’s been a staple in studios and live setups for decades.
- Korg minilogue xd: Combines powerful synthesis with a vocoder for creative sound design.
- Best For: Beginners and professionals looking for an affordable, versatile synth/vocoder combo.
3. Electro-Harmonix
- Why It’s Great: Known for their unique approach to effects, Electro-Harmonix creates vocoders with distinctive character and high-quality performance.
- Popular Models:
- Electro-Harmonix V256: A versatile and compact vocoder pedal with built-in pitch correction and gender control.
- Electro-Harmonix Voice Box: A multi-functional vocal effects processor with vocoder capabilities.
- Best For: Guitarists and vocalists looking for creative, pedalboard-friendly options.
4. Moog
- Why It’s Great: Moog is synonymous with premium analog synthesizers and vocoders, offering unmatched sound quality.
- Popular Model:
- Moog Vocoder (16 Channel): A true analog vocoder with exceptional clarity and vintage character.
- Best For: Audiophiles and synthesizer enthusiasts who demand top-tier analog quality.
5. TC-Helicon
- Why It’s Great: Specializes in vocal effects processors designed for live performances and studio use.
- Popular Models:
- TC-Helicon VoiceLive Touch 2: A versatile vocal effects processor with a vocoder, harmonizer, and looping capabilities.
- TC-Helicon Perform-VE: A compact unit for real-time vocal effects and vocoding.
- Best For: Live performers who need intuitive and portable vocal processing.
Bonus: Software Vocoders
If you’re open to software options, consider plugins like:
- Native Instruments Razor (for unique vocoder sounds in electronic music).
- XILS 5000 (emulating vintage analog vocoders).
- iZotope VocalSynth (a versatile and modern vocoder with creative effects).
Conclusion
The vocoder is more than just a tool for creating robotic voices; it is a bridge between the human and the machine, enabling musicians to explore uncharted sonic territories. From its origins in telecommunications to its role in shaping modern music, the vocoder has proven to be a versatile and enduring piece of technology. Whether used by electronic pioneers like Kraftwerk or modern innovators like Bon Iver, the vocoder continues to inspire creativity and push the boundaries of sound.