The oud, often referred to as the “king of instruments,” is a captivating and versatile stringed instrument with a rich history spanning centuries. Originating from the Middle East, the oud has transcended cultural boundaries to become an integral part of music across the globe. In this article, we embark on a musical journey to explore the origins, characteristics, and significance of the oud.

What is an Oud?
Oud Origin and History:
The oud’s roots can be traced back thousands of years to ancient Mesopotamia, making it one of the oldest known stringed instruments. Over time, it spread throughout the Arab world, eventually reaching Europe during the Moorish conquests of Spain. The oud’s influence extended to various musical traditions, including those in North Africa, Turkey, Persia, and beyond.
Oud Characteristics and Construction:
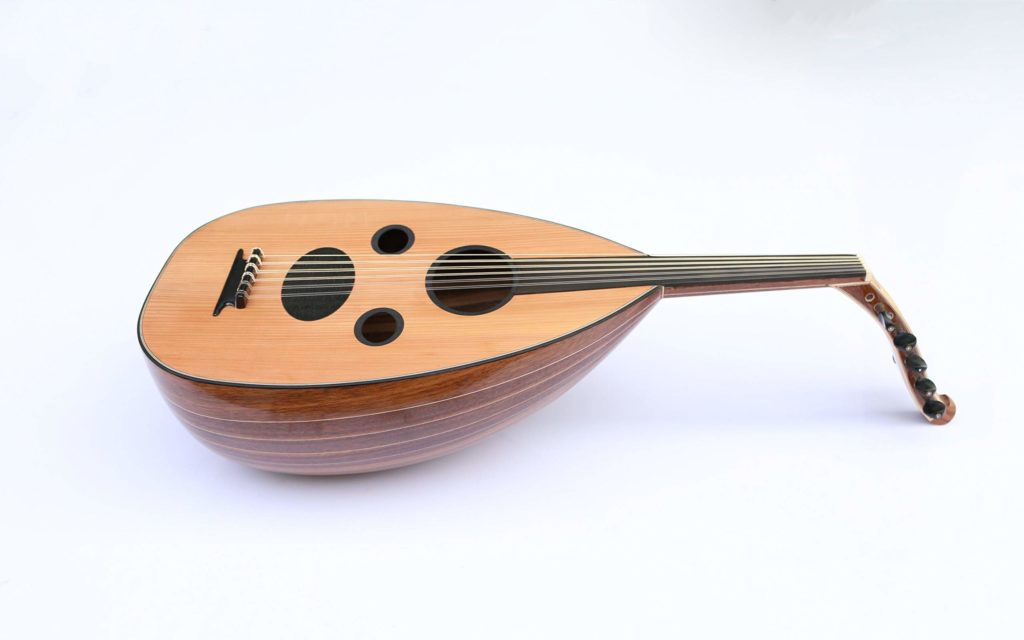
The oud features a deep, pear-shaped body and a short neck with no frets, allowing for microtonal flexibility. Traditionally, it has eleven strings, grouped in pairs except for the lowest string. The strings are made of nylon or gut, and the soundboard is often constructed from spruce or cedar. The oud’s unique design and craftsmanship contribute to its distinct sound and playability.
Oud Versatility and Musical Expression:
The oud is celebrated for its ability to convey a wide range of emotions and moods. Its melodic and rhythmic possibilities make it suitable for both solo and ensemble performances. Musicians explore various playing techniques, including fingerpicking, strumming, and sliding, to create intricate melodies and harmonies. The oud’s expressive qualities have made it a staple in genres like classical Arabic music, Turkish music, Persian music, and even fusion styles.
Oud Cultural Significance:
Beyond its musical prowess, the oud holds great cultural significance. It is deeply intertwined with the cultural heritage of the Middle East and North Africa. The oud has played a vital role in storytelling, celebrations, and religious ceremonies throughout history. Its presence in these cultural contexts has allowed for the preservation and transmission of traditions across generations.
Oud Contemporary Influence:
The oud’s influence has transcended its original geographical boundaries, captivating musicians and audiences worldwide. It has found a place in various musical genres, including jazz, world music, and contemporary fusion. Musicians such as Rabih Abou-Khalil, Anouar Brahem, and Simon Shaheen have embraced the oud, blending it with diverse musical styles and pushing the boundaries of its potential.
Preserving the Tradition:
In recent years, there has been a renewed interest in the oud, both among seasoned musicians and aspiring enthusiasts. Organizations, workshops, and festivals dedicated to the oud have emerged globally, fostering the preservation of traditional playing techniques, compositions, and improvisation methods. Through these efforts, the oud continues to thrive and evolve, bridging cultures and fostering musical dialogue.
In conclusion, the oud stands as a testament to the enduring power of music to transcend borders and touch the depths of human emotion. Its ancient origins and enduring legacy highlight its status as a truly remarkable instrument. Whether played in a traditional setting or blended with contemporary styles, the oud remains a captivating symbol of cultural heritage and artistic expression.
More Articles
Charango Tabs
Banjo Tabs
Lute Tabs
Dobro Tabs
Mandolin Tabs
Ukulele Tabs
Harmonica Tabs
Drum Tabs
Dulcimer Tabs
Bouzouki Tabs
What is a Sanxian?