Nestled within the vibrant tapestry of Moroccan music lies the sintir, a captivating three-stringed lute that pulsates with a hypnotic rhythm and a hauntingly beautiful sound. More than just an instrument, the sintir is a cultural cornerstone, deeply intertwined with the Gnawa people’s rich heritage and spiritual practices. This article delves into the world of the sintir, exploring its history, construction, playing techniques, and the vital role it plays in Gnawa music.
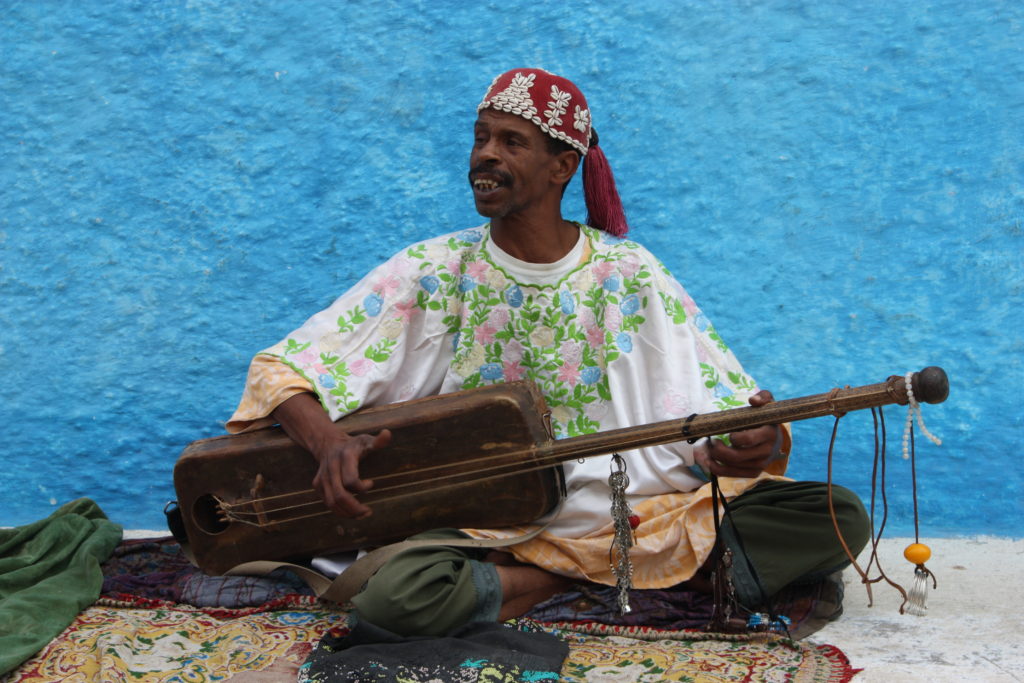

What is a Sintir?
A Legacy Rooted in the Sands of Time:
The exact origins of the sintir remain shrouded in some mystery. However, several theories suggest its connection to similar instruments found across North and West Africa. Some believe it descended from lutes like the Hausa halam (Nigeria) or the ngoni (Mali), brought to Morocco by enslaved people from Sub-Saharan Africa. This connection resonates with the Gnawa people’s own history. Descended from West African populations brought to Morocco through the trans-Saharan slave trade, the Gnawa people have preserved a unique cultural identity that blends Islamic traditions with West African musical influences. The sintir became a powerful instrument for them, expressing their heritage and stories through its resonant melodies.
Crafted with Care: A Look at the Sintir’s Anatomy:
The sintir is a captivating instrument, both visually and aurally. Here’s a breakdown of its key components:
- Body: Traditionally carved from a single piece of wood, often cedar or juniper, the sintir’s body boasts a rectangular shape. This resonating chamber amplifies the vibrations from the strings.
- Camel Skin: The front of the body, called the tabla, is adorned with cured camel skin, acting similarly to the drumhead on a banjo. This skin plays a crucial role in the instrument’s percussive character.
- Neck: A simple wooden neck protrudes from the body, supporting the strings and providing a platform for the player’s fingers.
- Strings: Three goat gut or nylon strings, traditionally tuned in a pentatonic scale, are stretched across the length of the neck. Some modern sintirs use tuning pegs, while others maintain the tradition of securing strings with knots.
- Metal Jingle: Often attached to the end of the neck, a metal rattle adds a distinct percussive element when the sintir is played.
A Tapestry of Techniques: Bringing the Sintir to Life:
The sintir’s magic lies not just in its construction but also in the unique playing techniques employed by Gnawa musicians, known as maâlems. Here are some key aspects of sintir playing:
- Plucking and Strumming: The strings are primarily plucked with the thumb or fingers, creating a rhythmic foundation that complements the singing and hand clapping.
- Percussive Power: The player often strikes the camel skin with their knuckles, adding a percussive element that blends seamlessly with the plucked notes. This technique creates a unique, rhythmic interplay between the skin and the strings.
- Vibrato and Ornamentation: Skilled maâlems employ subtle finger movements to add vibrato and ornamentation to the notes, enriching the melodic tapestry.
The Soul of Gnawa Music: Where the Sintir Reigns Supreme:
The sintir is the undisputed heart of Gnawa music, also known as Gnaoua. This enthralling musical genre is characterized by:
- Hypnotic Rhythms: The sintir’s pulsating rhythm provides a hypnotic foundation that guides the entire ensemble.
- Repetitive Melodies: Simple, repetitive melodies played on the sintir interweave with the haunting vocals of the maâlem and the rhythmic hand clapping (krakeb) of the other musicians.
- Spiritual Trance: Gnawa ceremonies often aim to reach a state of trance, where participants connect with their ancestors and seek spiritual healing. The sintir’s mesmerizing rhythms play a vital role in inducing this trance-like state.
Beyond Gnawa: The Sintir’s Expanding Horizons:
While deeply rooted in Gnawa music, the sintir’s captivating sound has begun to bridge cultural boundaries. Modern musicians across the globe are incorporating the sintir’s unique sound into their music, exploring its potential in a wider range of genres. This cross-pollination has led to a resurgence of interest in the instrument and its rich history.
Learning the Sintir: A Journey Through Sound and Tradition:
If the sintir’s music has piqued your interest, you might be curious about embarking on your own sonic journey. Finding a skilled Gnawa maâlem or a teacher familiar with the instrument can take time and dedication. However, with perseverance, online resources and instructional materials are increasingly available to help you learn the basics. Remember, mastering the sintir is more than just learning notes and techniques; it’s about understanding the cultural context and the spirit of Gnawa music.
The Future of the Sintir: A Legacy Enduring:
The sintir’s future seems bright. As Gnawa music continues to captivate audiences worldwide, the sintir remains the beating heart of this cultural expression. Its unique sound serves as a bridge between past and present, connecting generations and fostering a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of Moroccan music. From intimate Gnawa ceremonies to the global stage, the sintir’s voice continues to resonate, a testament to the enduring power of tradition and the beauty of musical expression.
Beyond the Text: Exploring the Sintir Further:
- Listen to Gnawa Music: Immerse yourself in the world of Gnawa music. Platforms like YouTube and music streaming services offer a wealth of recordings featuring the sintir. Artists like Maalem Mahmoud Gania, Nass El Ghiwane, and Groupe National Gnaoua are excellent starting points.
- Visit Morocco: If the opportunity arises, experiencing Gnawa music live in Morocco is an unforgettable experience. Witnessing the sintir played in its cultural context offers a profound appreciation for its power and significance.
- Support Gnawa Artists: Many Gnawa musicians face challenges in preserving their traditions. Consider supporting them by purchasing their music or attending live performances when possible.
The sintir is more than just an instrument; it’s a cultural treasure that embodies the rich tapestry of Gnawa music. Its captivating sound continues to resonate, fostering a deeper connection with Morocco’s vibrant heritage and the power of music to transcend borders and touch the soul. So, the next time you hear the sintir’s mesmerizing melody, take a moment to appreciate this unique instrument and the cultural legacy it represents.
Banjo Tabs
Lute Tabs
Dobro Tabs
Mandolin Tabs
Ukulele Tabs
Harmonica Tabs
Drum Tabs
Dulcimer Tabs
Bouzouki Tabs
What is a Sanxian?
What is an Oud?
Oud Tabs and Tablature